« Previous « Start » Next »
5 Geometric Programming (GP)
The
primal GP is :
|
|
|
|
| (GP) |
VGP:= |
minimize |
g0(t) |
|
| |
|
subject to |
gk(t) ≤ 1, |
k = 1,2,…, p |
| |
|
|
ti > 0, |
i = 1,2,…, m |
|
|
|
|
(1) |
|
where
|
|
| g0(t) |
= |
|
(2) |
| gk(t) |
= |
| |
|
cj t1a1j ... tmamj,
k = 1,2,…, p.
|
|
(3) |
|
Given exponents
aij for the
ith variable in the
jth product term,
i=1,…,
m and
j=1,…,
np, are arbitrary real constants and
term coefficients
cj are positive.
Here,
g0(
t) is called the objective function and
gk(
t) the
kth
constraint function, where
n0 is the number of product terms in the objective function and
(
nk−
nk−1) is the number of product terms in the
k constraint function.
Therefore, the number of the total product terms is
np, where
p is
the number of constraint functions.
The vector
t contains
m variables, denoted by
t1,…,
tm.
The program solves
posynomial GP, and so we shall remove
posynomial with this understanding.
The dual to
GP ([
8]) is
|
|
|
|
| (GD) |
VGD:= |
maximize |
|
| |
| |
|
subject to |
|
| |
| |
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
xj ≥ 0, j=1,2,…, np |
|
|
|
|
(4) |
|
where
For a (primal)
GP having
m variables (
ti),
p constraints and
np
(posynomial) product terms we see that (dual)
GD has
np non-negative
variables (
xj) in
m+1 linear equations. In the literature the
degree of difficulty of a
GP is defined by :
|
|
|
degree of difficulty = np − m − 1.
|
|
|
(6) |
|
Let
F(
x) denote the negative of the logarithm of the objective function
of (
GD), i.e.,
|
|
| |
F(x) = |
|
xj ln( |
|
)
+ |
|
|
|
xj
ln( |
|
).
|
|
|
|
(7) |
|
We see that (
GD) is a linearly constrained
convex programming problem,
| |
minimize |
F(x) |
|
| |
subject to |
A x = b, |
x ≥ 0, |
|
where the coefficient matrix is given by
|
|
| A =
|
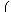
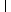
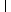
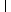
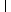
 |
| 1 |
... |
1 |
0 |
... |
0 |
... |
0 |
... |
0 |
| a1,1 |
... |
a1,n0 |
a1, n0+1 |
... |
a1, n1 |
... |
a1,np−1+1 |
... |
a1, np |
| ... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
... |
| am,1 |
... |
am,n0 |
am,n0+1 |
... |
am,n1 |
... |
am,np−1+1 |
... |
am,np |
| ,
|
|
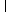
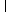
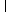
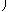 |
|
|
|
|
(8) |
|
and right side hand
|
|
bT = (1, 0,...,0)  R m+1 . R m+1 .
|
|
|
(9) |
|
Note that the first
n0 entries of the first row of
A are ones,
and data
aij are stored from row 2 to row
m+1 in
A.
« Previous « Start » Next »