« Previous « Start » Next »
15 Linear Semi-Definite w BMI
In
bmi_prob there is 1 linear semi-definite programming problem with bilinear matrix inequalities
with 3 variables.
In order to define this problem and solve it execute the following in Matlab:
Prob = probInit('bmi_prob',1);
Result = tomRun('',Prob);
An example of a problem of this class,
(that is also found in the TOMLAB quickguide) is glbQG:
|
|
Q0i + |
|
n Qkixk + |
|
n |
|
n xkxlKkli 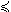 0 (17) 0 (17) |
The following file illustrates how to define and solve a problem
of this category in TOMLAB.
File: tomlab/quickguide/bmiQG.m
% bmiQG is a small example problem for defining and solving
% semi definite programming problems with bilinear matrix
% inequalities using the TOMLAB format.
Name='bmi.ps example 3';
A = [];
b_U = [];
b_L = [];
c = [ 0 0 1 ]; % cost vector
% One matrix constraint, set linear part first
SDP = [];
% The constant matrix is stored as
% SDP(i).Q{j} when SDP(i).Qidx(j) == 0
SDP(1).Q{1} = [-10 -0.5 -2 ;-0.5 4.5 0 ;-2 0 0 ];
SDP(1).Q{2} = [ 9 0.5 0 ; 0.5 0 -3 ; 0 -3 -1 ];
SDP(1).Q{3} = [-1.8 -0.1 -0.4 ; -0.1 1.2 -1 ; -0.4 -1 0 ];
% Sparse is fine, too. Eventually, all the matrices are
% converted to sparse format.
SDP(1).Q{4} = -speye(3);
SDP(1).Qidx = [0; 1; 2; 3];
% Now bilinear part
% K_12 of constraint 1 (of 1) is nonzero, so set in SDP(i).K{1}.
SDP(1).K{1} = [0 0 2 ; 0 -5.5 3 ; 2 3 0 ];
SDP(1).Kidx = [1 2];
n = length(c);
x_L = [-5 ; -3 ; -Inf];
x_U = [ 2 ; 7 ; Inf];
x_0 = [ 0 ; 0 ; 0 ];
f_Low = [];
Prob = bmiAssign([], c, SDP, A, b_L, b_U, x_L, x_U, x_0,...
Name, f_Low);
Result = tomRun('penbmi', Prob, 1);
« Previous « Start » Next »