« Previous « Start » Next »
83 Path Tracking Robot
User’s Guide for DIRCOL
2.7 Optimal path tracking for a simple robot. A robot with two rotational joints and simplified equations of motion has to move along a prescribed path with constant velocity.
83.1 Problem Formulation
Find u over t in [0; 2 ] to minimize
| J = | ∫ | | ( | | (wi*(qi(t) − qi,ref)2) + | | (w2+i*( | | i(t) − | | i,ref)2) dt |
subject to:
A transformation gives:
| x1:4(2) = [0.5 0.5 0 0.5] |
| x11,ref = | | (0<t<1), | | (1<t<2) |
| x21,ref = 0 (0<t<1), | | (1<t<2) |
| x31,ref = | | (0<t<1), 0 (1<t<2) |
| x41,ref = 0 (0<t<1), | | (1<t<2) |
Reference: [33]
83.2 Problem setup
toms t
p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, 2, 100, [], 'fem1s'); % Use splines with FEM constraints
%p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, 2, 100, [], 'fem1'); % Use linear finite elements
%p = tomPhase('p', t, 0, 2, 100); % Use Gauss point collocation
setPhase(p);
tomStates x1 x2 x3 x4
tomControls u1 u2
% Box constraints
cbox = {
-10 <= collocate(u1) <= 10
-10 <= collocate(u2) <= 10};
% Boundary constraints
cbnd = {initial({x1 == 0; x2 == 0
x3 == 0.5; x4 == 0})
final({x1 == 0.5; x2 == 0.5
x3 == 0; x4 == 0.5})};
% ODEs and path constraints
w1 = 100; w2 = 100;
w3 = 500; w4 = 500;
err1 = w1*(x1-t/2.*(t<1)-1/2*(t>=1)).^2;
err2 = w2*(x2-(t-1)/2.*(t>=1)).^2;
err3 = w3*(x3-1/2*(t<1)).^2;
err4 = w4*(x4-1/2*(t>=1)).^2;
toterr = integrate(err1+err2+err3+err4);
ceq = collocate({
dot(x1) == x3
dot(x2) == x4
dot(x3) == u1
dot(x4) == u2});
% Objective
objective = toterr;
83.3 Solve the problem
options = struct;
options.name = 'Path Tracking Robot';
solution = ezsolve(objective, {cbox, cbnd, ceq}, [], options);
t = subs(icollocate(t),solution);
x1 = subs(icollocate(x1),solution);
x2 = subs(icollocate(x2),solution);
x3 = subs(icollocate(x3),solution);
x4 = subs(icollocate(x4),solution);
u1 = subs(icollocate(u1),solution);
u2 = subs(icollocate(u2),solution);
Problem type appears to be: qp
Starting numeric solver
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2011-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: 1: Path Tracking Robot f_k 1.031157513483037700
sum(|constr|) 0.000000051263199492
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 1.031157564746237200
f(x_0) 0.000000000000000000
Solver: CPLEX. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
CPLEX Barrier QP solver
Optimal solution found
FuncEv 10 GradEv 10 ConstrEv 10 Iter 10
CPU time: 0.343750 sec. Elapsed time: 0.235000 sec.
83.4 Plot result
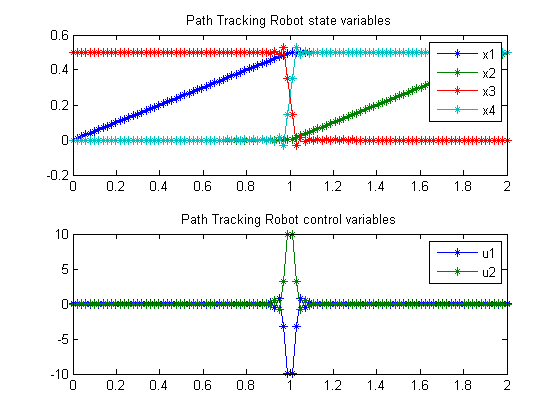
subplot(2,1,1);
plot(t,x1,'*-',t,x2,'*-',t,x3,'*-',t,x4,'*-');
legend('x1','x2','x3','x4');
title('Path Tracking Robot state variables');
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(t,u1,'*-',t,u2,'*-');
legend('u1','u2');
title('Path Tracking Robot control variables');
« Previous « Start » Next »