« Previous « Start » Next »
122 Two-Phase Schwartz
Users Guide for dyn.Opt, Example 4
Schwartz, A. L., Theory and Implementation of Numerical Methods based on Runge-Kutta Integration for Solving Optimal Control Problems. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of California, Berkeley, 1989
122.1 Problem Formulation
Find u over t in [0; 2.9 ] to minimize
| J = 5*(x1(tF)2 + x2(tF)2) |
subject to:
and path constraints for t<1:
| −0.8−x2 <= 0 –> −0.8 <= x2 |
Reference: [16]
122.2 Problem setup
toms t1
p1 = tomPhase('p1', t1, 0, 1, 25);
toms t2
p2 = tomPhase('p2', t2, 1, 1.9, 25);
setPhase(p1);
tomStates x1p1 x2p1
tomControls up1
setPhase(p2);
tomStates x1p2 x2p2
tomControls up2
setPhase(p1);
% Initial guess
x01 = {icollocate({x1p1 == 1; x2p1 == 1})
collocate(up1==0)};
% Box constraints
cbox1 = {-0.8 <= icollocate(x2p1)
-1 <= collocate(up1) <= 1};
% Boundary constraints
cbnd1 = initial({x1p1 == 1; x2p1 == 1});
% ODEs and path constraints
ceq1 = collocate({
dot(x1p1) == x2p1
dot(x2p1) == up1 - 0.1*(1+2*x1p1.^2).*x2p1
1-9*(x1p1-1).^2-((x2p1-0.4)/0.3).^2 <= 0});
setPhase(p2);
% Initial guess
x02 = {icollocate({x1p2 == 1; x2p2 == 1})
collocate(up2==0)};
% Box constraints
cbox2 = {-50 <= collocate(up2) <= 50};
% ODEs and path constraints
ceq2 = collocate({
dot(x1p2) == x2p2
dot(x2p2) == up2-0.1*(1+2*x1p2.^2).*x2p2});
% Link phase
link = {final(p1,x1p1) == initial(p2,x1p2)
final(p1,x2p1) == initial(p2,x2p2)};
% Objective
objective = 5*(final(p2,x1p2)^2+final(p2,x2p2)^2);
122.3 Solve the problem
options = struct;
options.name = 'Two Phase Schwartz';
constr = {cbox1, cbnd1, ceq1, cbox2, ceq2, link};
solution = ezsolve(objective, constr, {x01, x02}, options);
t = subs(collocate(p1,t1),solution);
t = [t;subs(collocate(p2,t2),solution)];
x1 = subs(collocate(p1,x1p1),solution);
x1 = [x1;subs(collocate(p2,x1p2),solution)];
x2 = subs(collocate(p1,x2p1),solution);
x2 = [x2;subs(collocate(p2,x2p2),solution)];
u = subs(collocate(p1,up1),solution);
u = [u;subs(collocate(p2,up2),solution)];
Problem type appears to be: qpcon
Starting numeric solver
===== * * * =================================================================== * * *
TOMLAB - Tomlab Optimization Inc. Development license 999001. Valid to 2011-02-05
=====================================================================================
Problem: --- 1: Two Phase Schwartz f_k -0.000000000000002541
sum(|constr|) 0.000000000002833381
f(x_k) + sum(|constr|) 0.000000000002830840
f(x_0) 10.000000000000014000
Solver: snopt. EXIT=0. INFORM=1.
SNOPT 7.2-5 NLP code
Optimality conditions satisfied
FuncEv 1 ConstrEv 24 ConJacEv 24 Iter 18 MinorIter 361
CPU time: 0.156250 sec. Elapsed time: 0.156000 sec.
122.4 Plot result
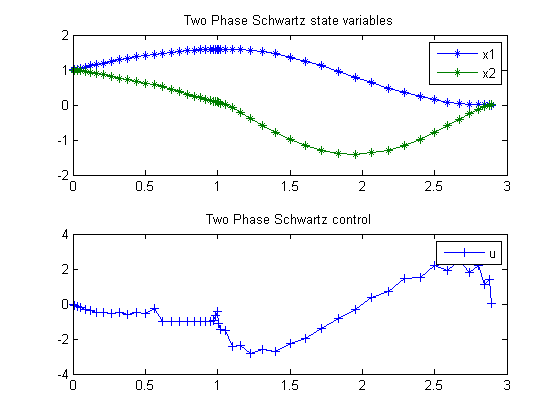
subplot(2,1,1)
plot(t,x1,'*-',t,x2,'*-');
legend('x1','x2');
title('Two Phase Schwartz state variables');
subplot(2,1,2)
plot(t,u,'+-');
legend('u');
title('Two Phase Schwartz control');
« Previous « Start » Next »